
STEAM, which stands for Science, Technology, Engineering, Art, and Mathematics, is a modern interdisciplinary education approach aimed at equipping learners with knowledge and skills from these five subjects. This model represents an upgraded version of the previous STEM education method, with the addition of the Art component, making it more comprehensive.
The STEAM education method originated from the creative idea of the Rhode Island School located in the United States. This lesson has gained positive feedback and is increasingly being adopted across the United States. Subsequently, STEAM has been applied in many developed countries worldwide and is considered one of the most advanced and widespread education methods today.
STEAM education provides students with an active and creative learning experience. Each lesson in the program involves real-life situations to stimulate students’ curiosity. As a result, students gradually enhance their skills, explore, and solve problems from various perspectives.
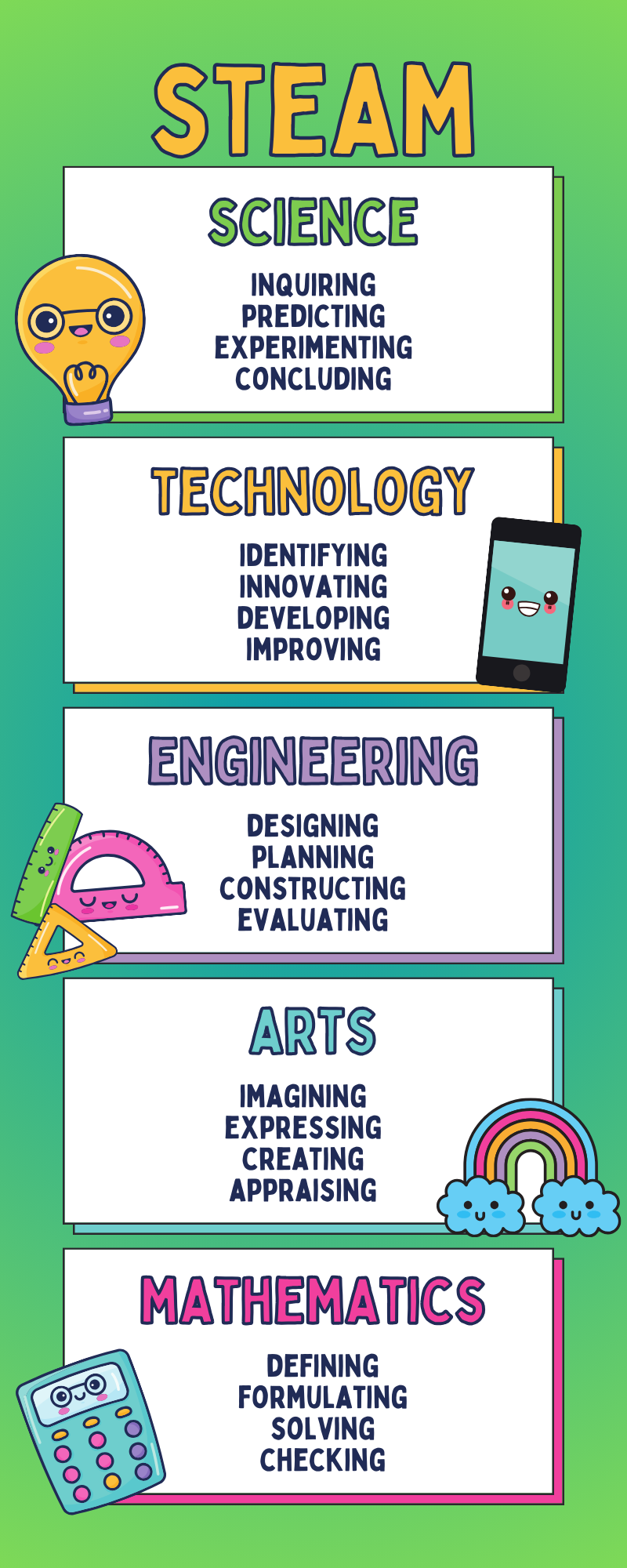
The STEAM approach helps children develop skills through the integration of various subjects such as mathematics, science, technology, engineering, and art. It enables students to acquire diverse and comprehensive knowledge while developing related skills, including:
Science (S): The STEAM model helps students understand the workings and connections between definitions and principles of objects and events. Based on this understanding, students can apply their knowledge to practice and solve real-life problems. For example, they might learn how rain is formed from water vapor.
Technology (T): Students are exposed to advanced and modern technology, allowing them to have a more accurate perception of science and technology. Through this, students can innovate and create scientific products and models, ranging from simple to complex.
Engineering (E): Integrating practical models into teaching helps students understand the production and operation of familiar products. This knowledge enables students to understand the basic principles of manufacturing and assembly, enhancing their creative thinking and problem-solving skills related to engineering. For instance, assembling simple robots or machines suitable for different age groups.
Art (A): Art is the distinguishing factor of the STEAM education model compared to STEM. In addition to emphasizing logical thinking, this method also helps students develop imaginative thinking. Learners have the freedom to create and explore the world of art, participating in activities such as music and painting to develop their senses and aesthetics. For example, dance is considered a subject that helps students cultivate observation skills, perseverance, and endurance.
Mathematics (M): Early STEAM education helps students become familiar with and practice numbers from a young age. It awakens their potential and passion for mathematics, building a solid foundation and accurate mathematical thinking, enhancing quick reflexes for practical application.
In summary, STEAM education is a holistic and innovative approach that encourages active and creative learning, fostering a range of skills in students across various disciplines.







